basic bank information
Ownership: Wholly owned by the Government of Kenya and does not involve public or private capital.
type: central bank, state-owned.
name and background<
ul style="list-style-type: disc" type="disc">full name: Central Bank of Kenya<
style="font-family: sans-serif; color: black">Founded: September 14,
1966 headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya
Shareholder Background: Wholly owned by the Government of Kenya, with no listed or privatized components.
Leadership structure: The current President is Dr. Kamau Thugge (appointed in June 2023) and the Vice Presidents are Dr. Susan Koech and Gerald Nyaoma. The President serves as the Chief Executive Officer and is responsible for the overall management and external communications of the Bank.
CBK was formerly known as the East African Currency Board (EACB), which managed the issuance of currencies in Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania during the British colonial period. In the mid-1960s, with the independence of the British colonies, the three East African countries wanted to manage their own monetary policy, which led to the dissolution of the EACB. In 1966, the Kenyan Parliament passed the Central Bank of Kenya Act, formally establishing the CBK, giving it the responsibility for currency issuance and financial supervision.
services and products
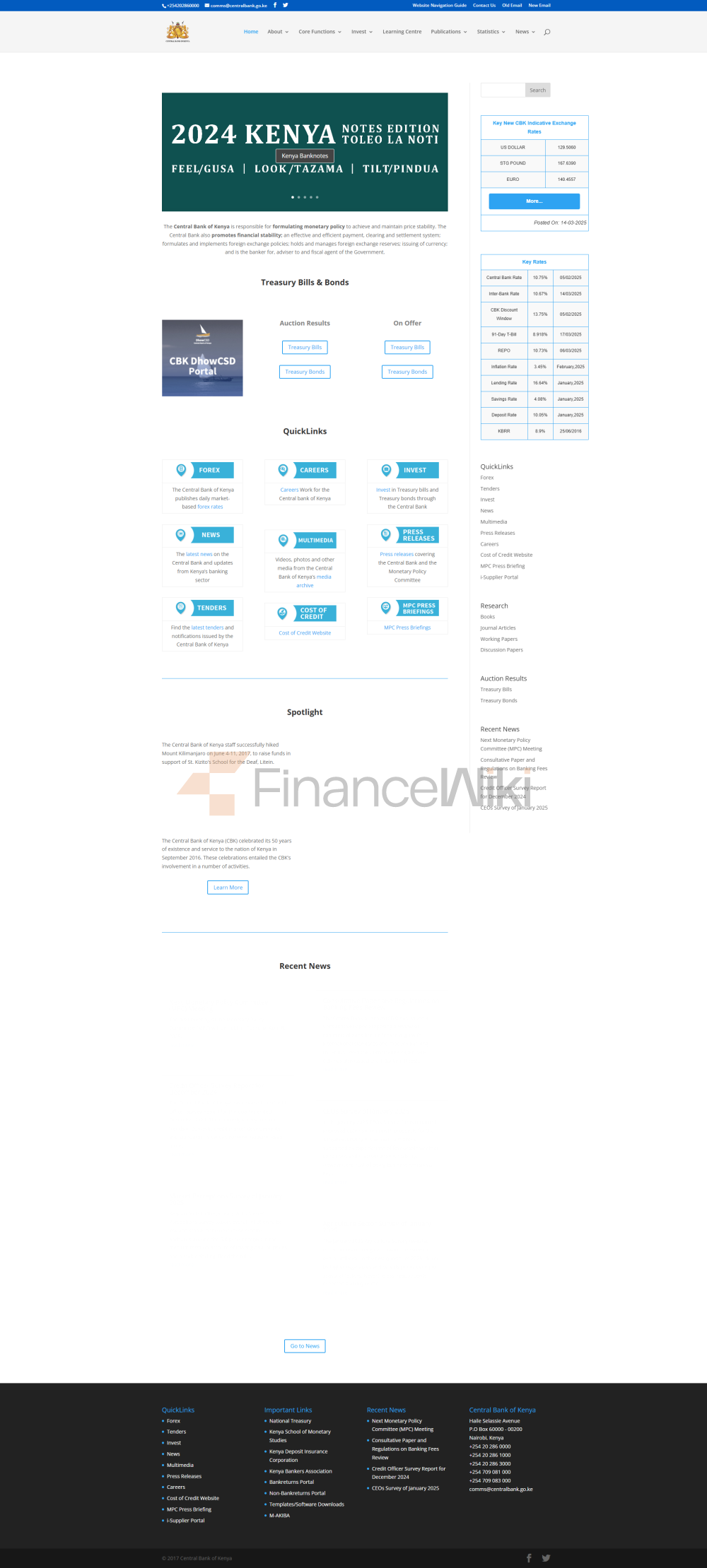
CBK's main functions include:
supervise the financial system and ensure the stability and compliance of banks and other financial institutions.
managed foreign exchange reserves, which are approximately US$9.6 billion as of November 2024, cover approximately 4.9 months of import needs.
issued Kenyan shillings (KES), which were responsible for the printing and circulation of the currency.
acts as a bank and fiscal agent for the government to manage the country's financial affairs.
promote financial inclusion and support the development of digital payments and microfinance.
> setting monetary policy, controlling inflation (target 2%-8%) and supporting economic growth.
CBK indirectly supports the financial services needs of individuals and businesses by regulating commercial banks and promoting payment systems.
financial health
CBK's financial health as a central bank is reflected in its reserve management and monetary policy effectiveness
key indicators:
> foreign exchange reserves: about US$9.6 billion in November 2024, covering 4.9 months of import needs, indicating strong currency stability.
Inflation rate: 4.11% in April 2025, within the target range (2%-8%), indicating that monetary policy is effective.
banking indicators: The capital adequacy ratio of the Kenyan banking sector in 2023 is about 21.5% (minimum requirement of 15%), and the non-performing loan ratio is 4.1% (less than 5%), reflecting the health of the financial system.
overall assessment: CBK's financial stability is backed by the government, and its foreign exchange reserves and policy execution capacity ensure economic stability, despite challenges to public debt and credit growth.
customer service
channel:
>Phone: +254 20 286 0000 (HQ)
Live chat: no explicit support, contact form available on the website.
Comments: Customer service is primarily for financial institutions and government departments, with the general public receiving indirect support through financial education activities such as the FinAccess Hukou Survey, which was launched in December 2024.
security measures
Technical security: data encryption and network security protocols are used to protect economic data and payment systems.
Physical security: Headquarters and branches are equipped with high standards of security to protect currency reserves and facilities.
Regulatory measures: Climate risk management guidelines will be issued in 2023 to require financial institutions to identify and manage environmental risks to ensure the stability of the financial system.
featured services and differentiations<
ul style="list-style-type: disc" type="disc">Monetary policy: control inflation and support economic growth by adjusting the central bank interest rate (10.00% on April 8, 2025).
Financial stability: monitoring banks' capital adequacy and risk management, May 2025 report shows banking sector health.
Foreign exchange reserves management: US$9.6 billion in reserves to support Kenyan shilling stability and safeguard international trade.
Financial Inclusion: Significant growth in the number of bank accounts in 2024 through FinAccess surveys and microfinance support to drive access to financial services.
International cooperation: Collaborate with the IMF, the World Bank, and others to share best practices and improve regional financial stability.